
Brugada Syndrome (canalopathy) Type 1 segmento 1 st elevado y onda T negativa Type 2 V2
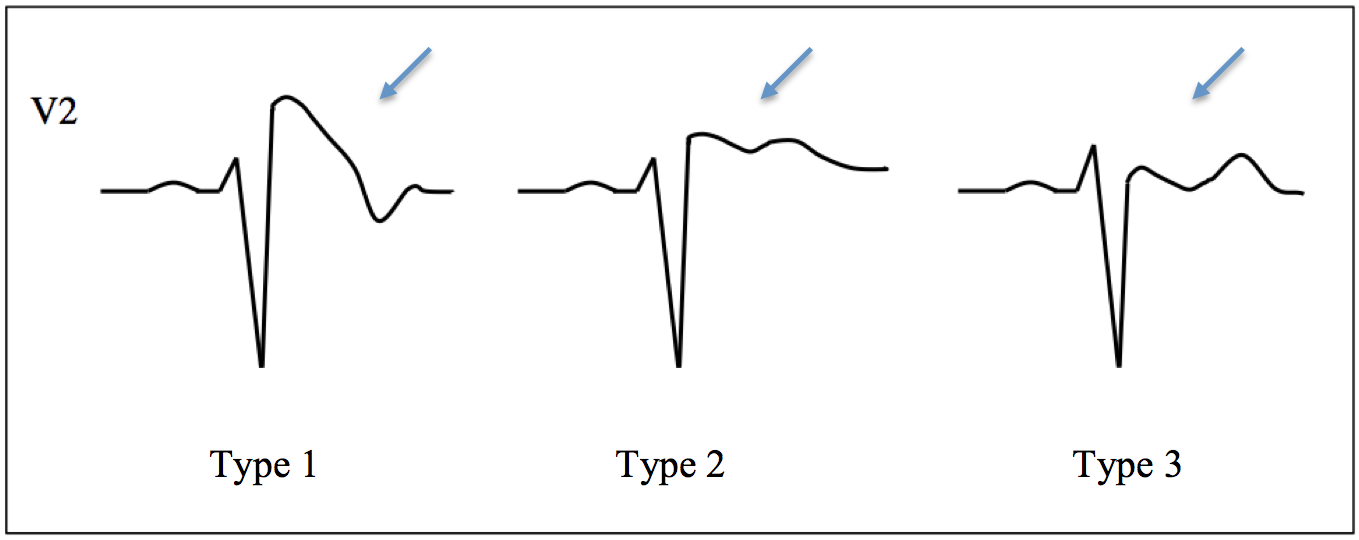
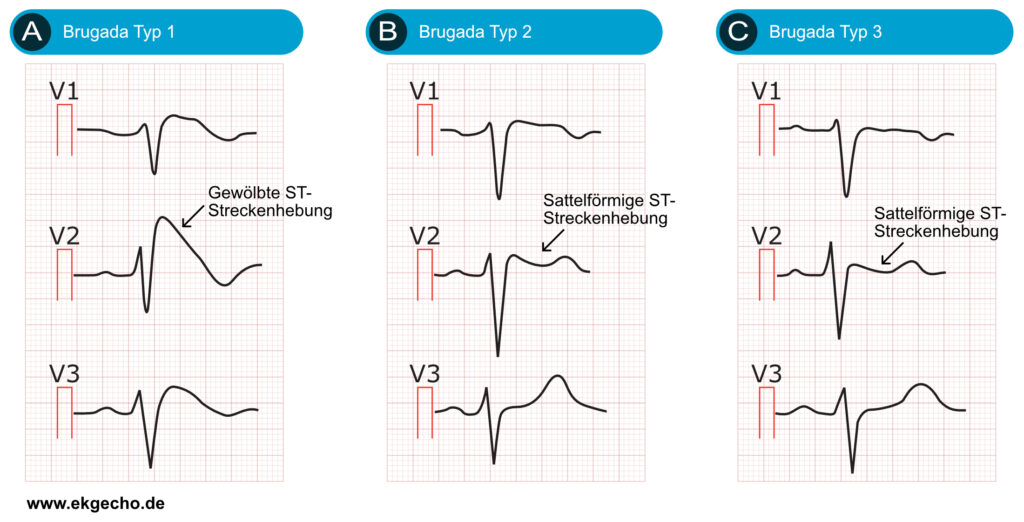
The other 2 types of Brugada are non-diagnostic but possibly warrant further investigation (see discussion below). Type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped ST elevation. Brugada Type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped ST elevation. Brugada Type 3 can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of ST segment elevation.

Figure 12 from Type 1 Brugada TypeECG Pattern Provoked by Fever in a Patient with COVID19
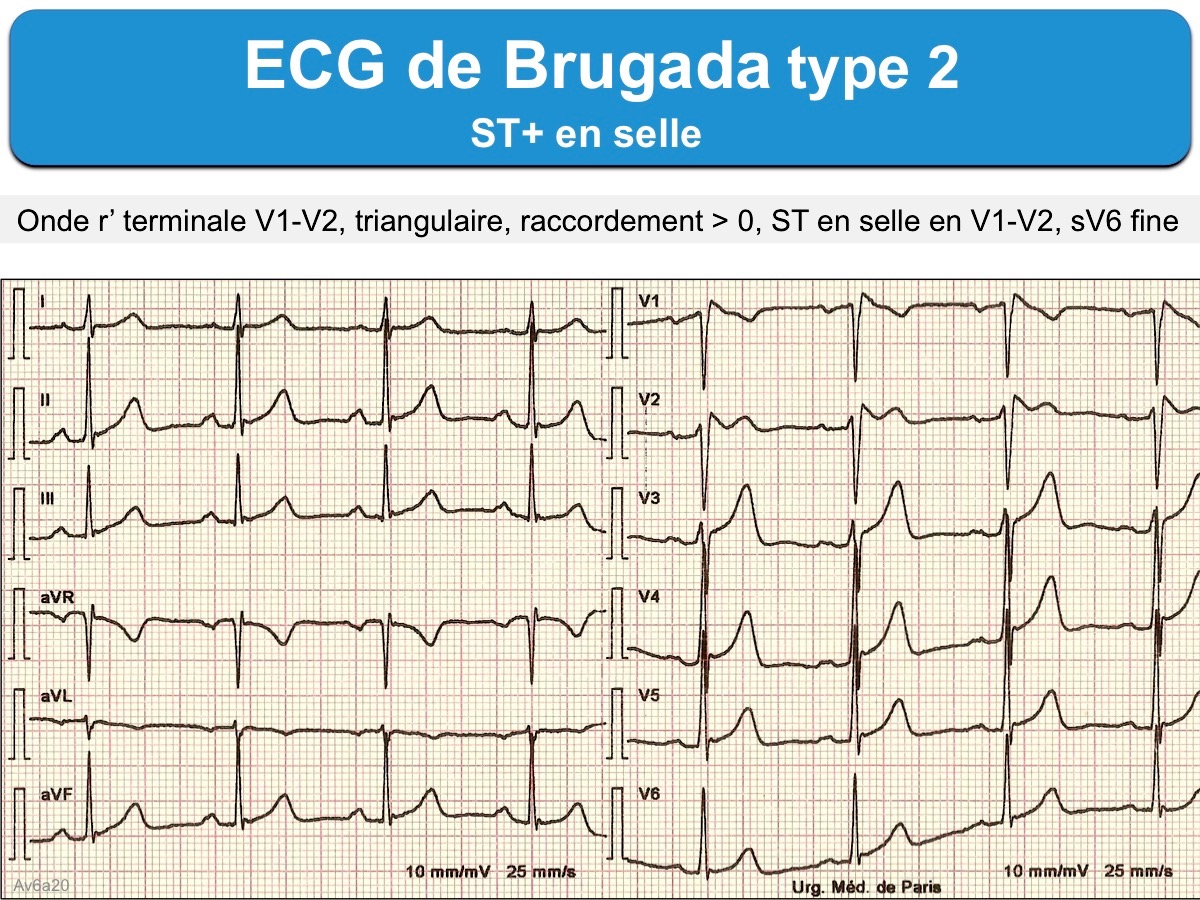
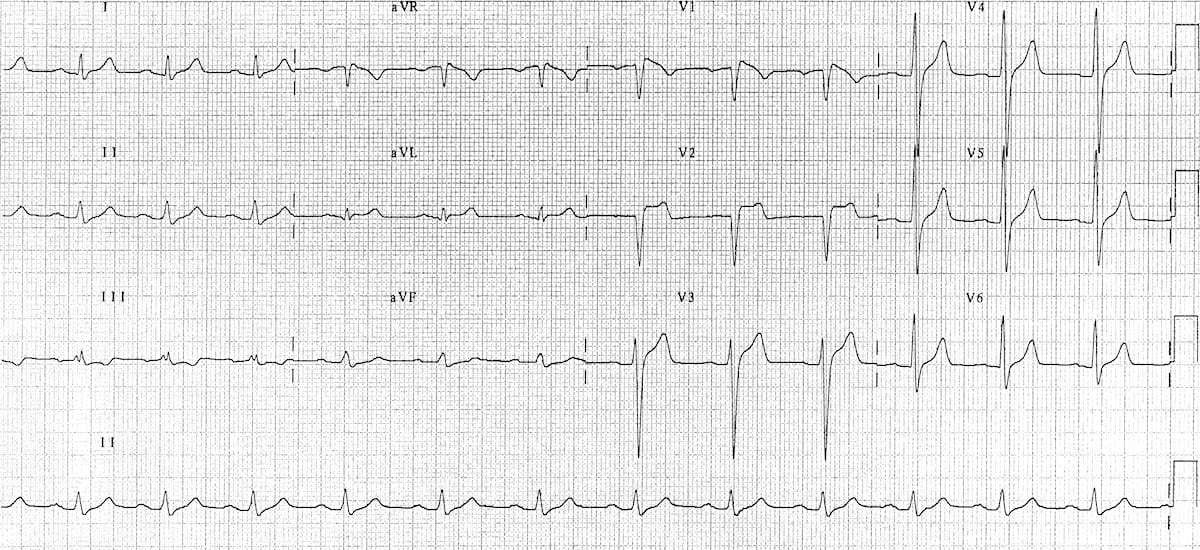
Step 1: Correct recognition of the diagnostic Brugada syndrome ECG pattern. 1) There is one true diagnostic of the Brugada pattern; two others may suggest the disease. Type 1: It is characterised by a prominent coved ST-segment elevation displaying J-point amplitude or ST-segment elevation ≥2 mm, followed by a negative T wave.

Feverinduced type 1 Brugada pattern Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia (English edition)
Initially, 3 ECG pattern types were described in patients with BrS, 75 although only type 1 changes are considered diagnostic . 77 A type 1 Brugada ECG consists of coved ST-segment elevation ≥2 mm with a negative T-wave in the right precordial leads, which are thought to be representative of pathophysiological changes in the RVOT. 36.

brugada ecg lead placement
Three forms of the Brugada ECG pattern have historically been described, although the Type 3 pattern is frequently merged with the Type 2 pattern in contemporary practice. Type 1 has a coved type ST elevation with at least 2 mm (0.2 mV) J-point elevation and a gradually descending ST segment followed by a negative T-wave.

(PDF) ECG interpretation in Brugada syndrome
Lesser degrees of these patterns (type 2 and type 3 Brugada ECG patterns) are not considered diagnostic. The type 2 and type 3 patterns may change to a type 1 pattern spontaneously, with fever, or in response to drugs. The latter is the basis of a challenge diagnostic test usually using IV ajmaline, procainamide, flecainide or pilsicainide.
ECG Brugada ecardiogram
Brugada syndrome is characterized by cardiac conduction abnormalities (ST segment abnormalities in leads V1-V3 on EKG and a high risk for ventricular arrhythmias) that can result in sudden death. Brugada syndrome presents primarily during adulthood, although age at diagnosis may range from infancy to late adulthood. The mean age of sudden death is approximately 40 years.

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Is this Type 2 Brugada syndrome/ECG pattern?
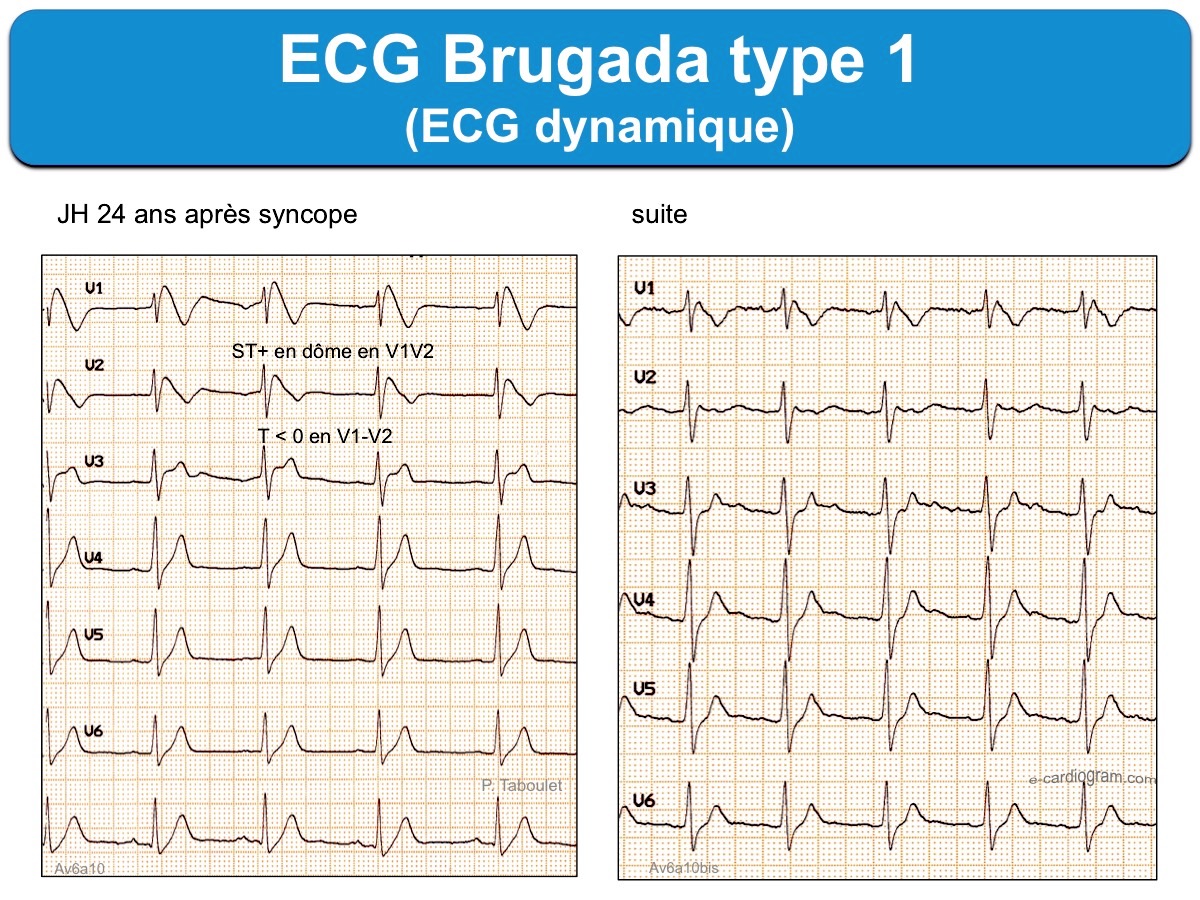
The type 1 Brugada ECG pattern is characterized by a complete or incomplete right bundle-branch block pattern with a coved morphology ST-segment elevation of at least 2 mm in the right precordial leads (V 1 -V 3) followed by a negative T wave. The type 2 ST-segment elevation has a saddleback appearance with a high takeoff ST-segment elevation.
ECG Brugada type 1 ou 2 ecardiogram
Brugada Type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped ST elevation. Type 3. Brugada type 3: can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of ST segment elevation. Management. The only proven therapy is an implantable cardioverter - defibrillator (ICD). Quinidine has been proposed as an alternative in settings where ICD's are.

ECG Brugada type 1 ou 2 ecardiogram
Signs and symptoms that may be associated with Brugada syndrome include: Dizziness. Fainting. Gasping and labored breathing, particularly at night. Irregular heartbeats or palpitations. Extremely fast and chaotic heartbeat. Seizures. A major sign of Brugada syndrome is an irregular result on an electrocardiogram (ECG), a test that measures the.

ECG Educator Blog Brugada Syndrome
Treatment for Brugada syndrome may include medication, catheter procedures or surgery to implant a device that controls the heartbeat. Brugada syndrome treatment depends on the risk of having a serious irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). Being at high risk involves having: A personal history of serious arrhythmias.
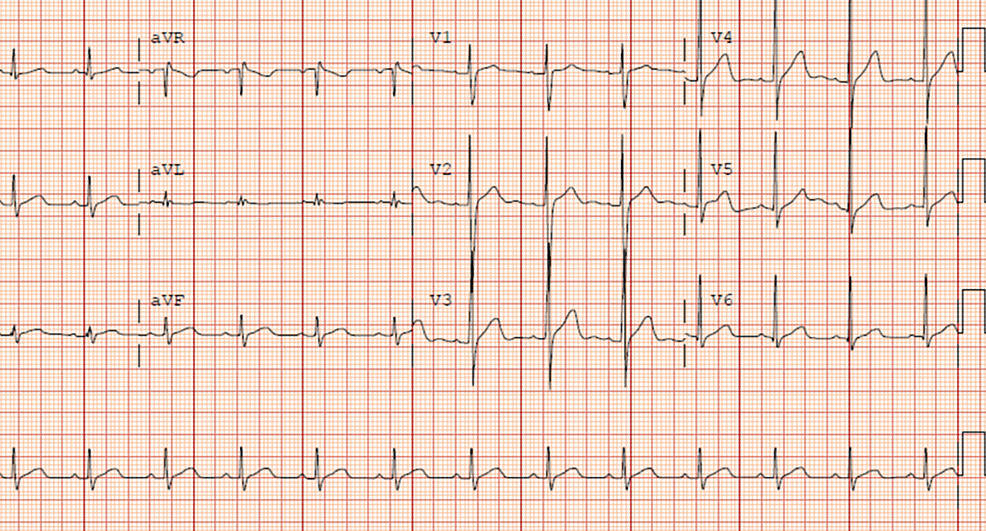
Cureus Brugada Pattern Type 2 Diagnosis Unmasked by Aspiration Pneumonia
2. Types of Brugada ECG patterns. Brugada patterns can be divided into two types (Fig. 1) .Type 1 pattern has a characteristic coved-shaped ST segment elevation (STE) ≥ 2 mm, J-point elevation, a gradually descending ST segment which terminates with a negative T-wave in the right precordial leads (V 1, V 2 and V 3) with or without a class I anti-arrhythmic drug challenge, such as flecainide .

Brugada syndrome should we be screening patients before prescribing psychotropic medication
A. Spontaneous type 1 Brugada ECG pattern at nominal or high: 3.5: B. Fever-induced type 1 Brugada ECG pattern at nominal or high leads: 3: C. Type 2 or 3 Brugada ECG pattern that converts w/ provocative drug challenge: 2 *Only award points once for highest score within this category. One item from this category must apply. II. Clinical History*
Brugada syndrome Australian Heart Disease Registry
Importance of ECG Phenotype Ascertainment. Although there has been general initial consensus about the ECG definition of Brugada ECG pattern into 3 types (type 1, type 2, and type 3), 4 there has been a recent effort to establish a more simplified mode of classification, including only 2 ECG patterns 6: pattern 1 identical to the classic type 1 of other consensus (coved pattern) and pattern 2.
Brugada Syndrome • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
Type 3 Brugada syndrome: Similar to type 2 criteria but the terminal portion of the ST segment is elevated <1 mm. Note that it is allowed to record the 12-lead ECG with the electrodes of leads V1 and V2 placed in the second, third, or fourth intercostal space to maximize the probability of detecting the ECG changes. This maneuver is recommended.

Type 1 Brugada Syndrome JETem
It is highly associated with ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death (SCD) in predominately middle-aged males. 1 The diagnosis is based on a particular ECG pattern described by the Brugada brothers in 1992. 2 There are 3 types of Brugada patterns. Our patient's ECG was consistent with type 1, which is diagnostic and is characterized.
BrugadaSyndrom EKG, klinische Merkmale und Management EKG & ECHO
The type 1 Brugada ECG pattern has prominent ST elevation in V1 and V2 (sometimes involving V3) that causes the QRS complex in these leads to resemble right bundle branch block. The ST segment is coved and descends to an inverted T-wave. The role of electrophysiologic testing is currently debated. Genetic testing is usually recommended but has.
- Bij Het Ontstaan Van De Wereld
- Hoeveel Canarische Eilanden Zijn Er
- Is Dit Soms Geen Zuivere Drank
- Hoogheemraadschap Hollands Noorderkwartier Stationsplein Heerhugowaard
- Canada Free Visa For Pakistani 2023
- Hoelang Duurt Een Pet Scan
- Something To Rely On Lyrics
- Eremedaille Orde Van Oranje Nassau
- Men S Evil Eye Bracelet Gold
- Elvis On America S Got Talent