
STA curves of microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel), the ionic liquid... Download Scientific Diagram
It is derived from plant sources: MCC is a purified form of cellulose, the main structural component of plant cell walls. Uses in supplements: MCC serves various purposes in supplements, including: Filler: Provides bulk to tablets and capsules without adding significant nutritional value. Binder: Helps hold ingredients together within a tablet.

SEM of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) particles showing that they are... Download Scientific
Microcrystalline cellulose is the same as cellulose, except that it meets USP standards. It is also found in many processed food products, and may be used as an anti-caking agent, stabilizer, texture modifier, or suspending agent among other uses. According to the Select Committee on GRAS Substances, microcrystalline cellulose is generally.

FTIR spectra of microcrystalline cellulose, cylindrical CNCs, spherical... Download Scientific
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is a versatile material with unique functional properties and is widely used in many areas including the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Despite being a known material for several decades, research interest and potential applications of MCC continue to grow, with huge global market potential..

Microcrystalline Cellulose HyperPharm
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is a term for refined wood pulp and is used as a texturizer, an anti-caking agent, a fat substitute, an emulsifier, an extender, and a bulking agent in food production. The most common form is used in vitamin supplements or tablets. It is also used in plaque assays for counting viruses, as an alternative to carboxymethylcellulose.

Solubility data of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), avicel cellulose... Download Scientific
Microcrystalline cellulose obtained from various types of cellulose sources of miscellaneous provenance using various extraction methods and conditions commonly differ in molecular weight, particle size, crystallinity, surface area, moisture content, porous structure, etc. 2.1.2. Microcrystalline cellulose isolations techniques

Characterization of biotinylated microcrystalline cellulose fibers.... Download Scientific Diagram
Is microkristallijne cellulose veilig? Ja, het is een veilige stof. Het is gewoon een onoplosbare vezel. Onoplosbare vezels nemen vocht op in de darm, wat betekent dat je er diarree van kan krijgen als je er heel erg veel van neemt. Van de hoeveelheden in supplementen zul je geen last krijgen. Bronnen.

Microcrystalline Cellulose // MCC 101, 102 // CAS9004346 biolla EN
Abrasive: Microcrystalline Cellulose acts as a gentle exfoliant in cosmetic products. It helps to remove dead skin cells and impurities from the skin surface, promoting a smoother and brighter complexion. This is achieved by the small, rough particles of Microcrystalline Cellulose, which provide a mild abrasive action when rubbed against the skin.

Structure of Microcrystalline Cellulose Synonyms Cellulose gel... Download Scientific Diagram
The major functions of Microcrystalline cellulose in food products as organoleptic enhancer are summarized. •. The food industry is the second biggest user of MCC after the pharmaceutical sector. •. MCC has nutraceutical functions and impact positively on the gastrointestinal physiology as well weight management. •.

REDWELLS® Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder Tablet Excipient
Microcrystalline cellulose in meat products is different, since the USDA regulates meat. The USDA has ruled that manufactured meat products can only contain 3.5 percent microcrystalline cellulose. Some argue that microcrystalline cellulose is just a redundant filler, but it is more expensive than carbohydrate fillers like sugar and starches.

The fundamental structural difference between cellulose and... Download Scientific Diagram
Microcrystalline waxes are a type of wax produced by de-oiling petrolatum, as part of the petroleum refining process. In contrast to the more familiar paraffin wax which contains mostly unbranched alkanes, microcrystalline wax contains a higher percentage of isoparaffinic (branched) hydrocarbons and naphthenic hydrocarbons. It is characterized by the fineness of its crystals in contrast to the.

Microcrystalline Cellulose
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is the most commonly used spheronizing aid in a formulation undergoing extrusion spheronization. It is available in different grades and particle sizes. Of all the different brands and grades of MCC, Avicel PH 101 or Emcocel 50 has been the most widely used. MCC helps in the formation of spheres because of its.

XRD spectra of the microcrystalline cellulose before and after pretreatment Download
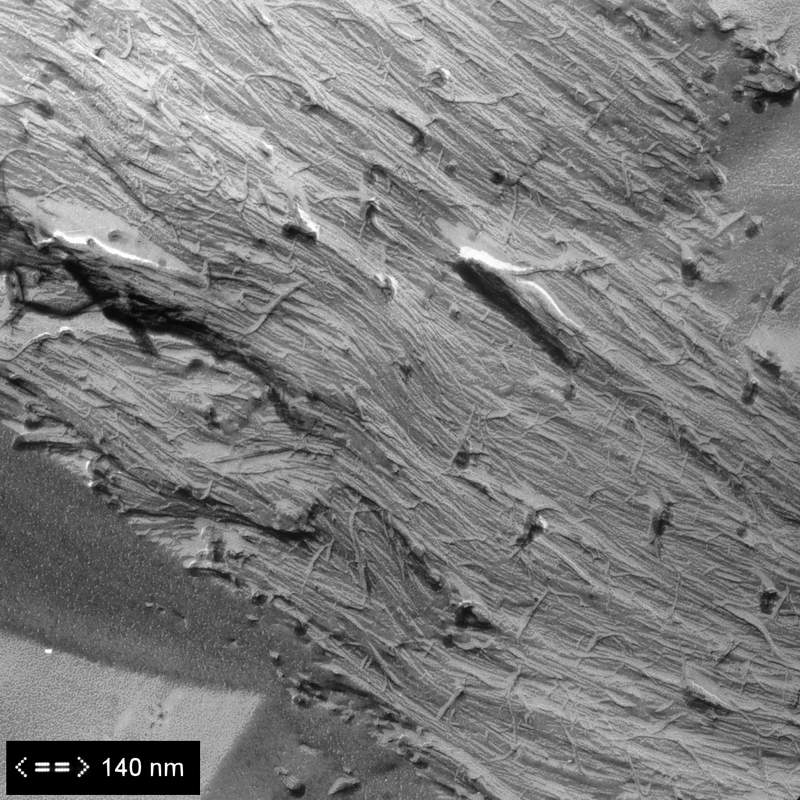
1. Introduction. Cellulose is the most abundant renewable biopolymer on Earth, which is unbranched, linear homopolysaccharide, composed of repeating β-(1 → 4) linked d-glucose units.During the last two decades, great research interest has been devoted to applying crystalline cellulose as a reinforcement material with other polymer matrixes due to its high thermal and mechanical stability.

MicrocrystallineCellulose
Microcrystalline cellulose or MCC is a pure-type crystalline cellulosic polysaccharide molecule bound by β-1,4-glucosidic bonds synthesized from the α-cellulose precursor. MCC is obtained from fibrous plant material, acid hydrolysis of cellulose using 2M hydrochloric acid at 105 °C for 15-20 minutes to reduce the degree of polymerization. It.
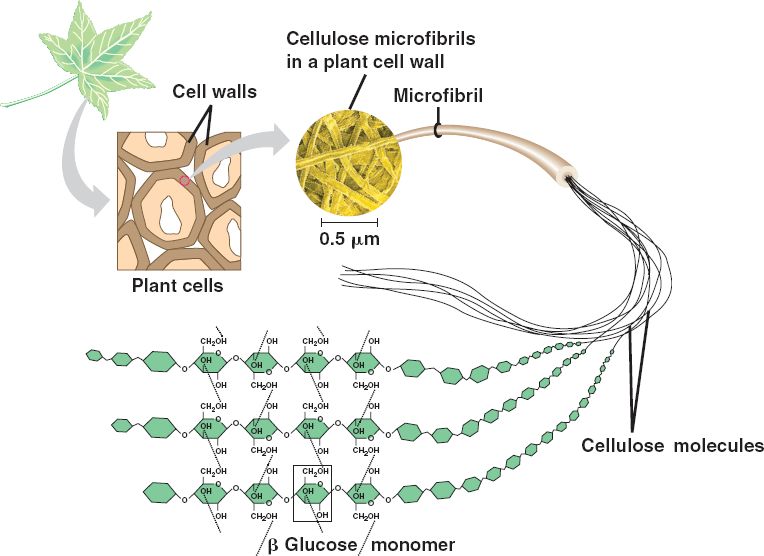
What is cellulose? + Example
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is obtained from naturally occurring cellulose that has been purified and partially depolymerized. MCC is an excipient with wide-ranging applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Particularly, in the process of extrusion-spheronization, MCC has shown unsurpassed efficiency in terms of process control and.
Microcrystalline cellulose with magnification 1000x shows the SEM... Download Scientific Diagram
Microcrystalline Cellulose Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) is an isolated, colloidal crystalline portion of cellu-lose fibers, deriving from partial depolymerization of the cellulose matrix, conventionally by treating cellulose with an excess of mineral acid. MCC can be co-processed with a water-soluble polymer to deliver a colloidal form or

8 (A) SEM micrographs of microcrystalline cellulose (Menta et al.,... Download Scientific Diagram
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is a partially purified depolymerized non-fibrous form of cellulose and it is a fine, white, odorless, crystalline powder and biodegradable material (Das et al. 2010). The recent research is focused on a wide range of underutilized lignocellulosic material as low price by converting waste products into value.
- Hoeveel Ounce Is Een Kilo
- What A Fool Believes Lyrics
- I Know What You Are Dog Meme
- Twee Vorstinnen En Een Vorst Peskens
- Leo Alkemade En Dochter In Reclame
- Wanneer Komt B B Vol Liefde
- Wat Vieren We Bij Pinksteren
- Kan Normale Friet In De Airfryer
- Partidos De Selección De Fútbol De Marruecos
- De Legende Van De Familie Vos